Optics
Light is a type of wave which follows many of the same rules as mechanical waves. Light refracts, diffracts, and reflects. Refraction is when a wave goes from one medium to another and bends. Diffraction is when they bend around corners. Reflections are when they bounce off what they are hitting. Light differs from mechanical waves as it does not need a medium (it can go through a vacuum).
Simulators and Calculators:
Use this wave simulator to visualize many of the setups listed below:
Use this to calculate the image position, scale and orientation:
Blue/black means real, green means virtual.
Here is yet a third simulator:
Here are some links to more simulators:
Here is a fifth. (Flat Mirror)
Here is a sixth. (Convex Mirror)
Here is a seventh. (Convex Lens)
Here is an eighth. (Concave Lens)
Here is a ninth. (Lens Combination)
Here is a tenth. (Diffraction Example)
Here is an 11th. (3D Diffraction Example)
Many more can be found at this web site.
Some of this is unrelated, but here is a link to many more math and science applets.
Refraction
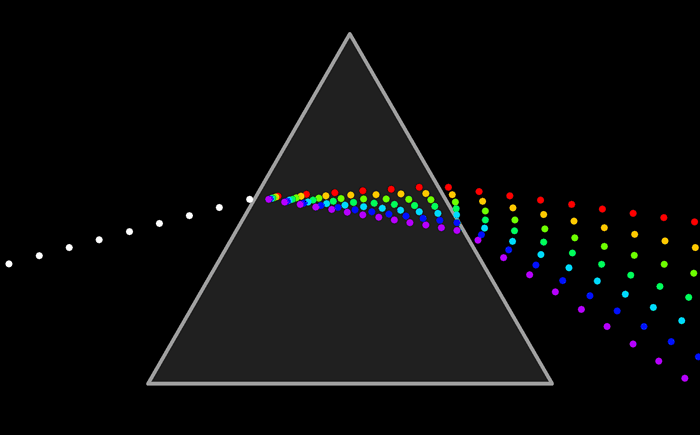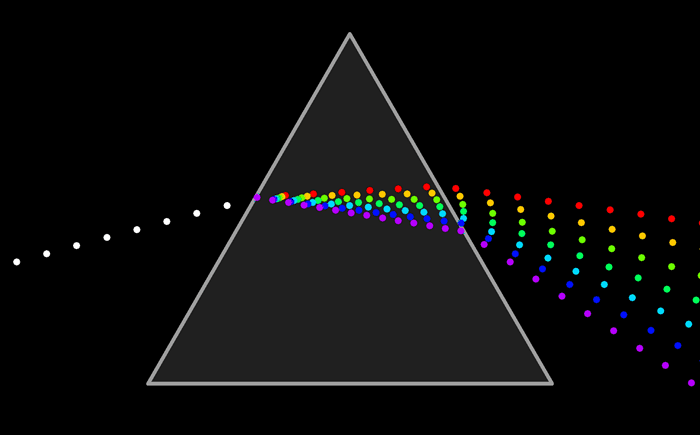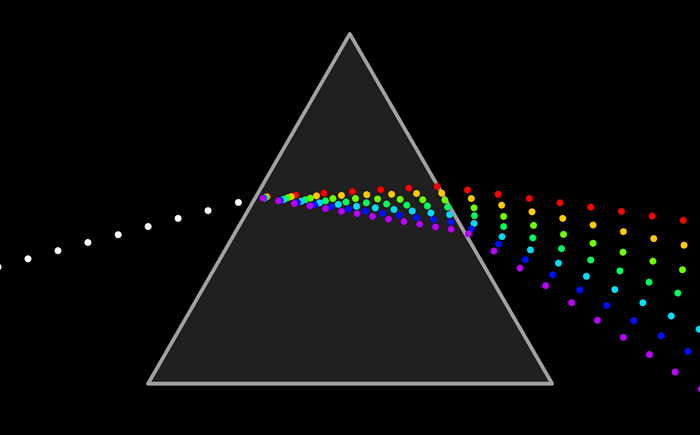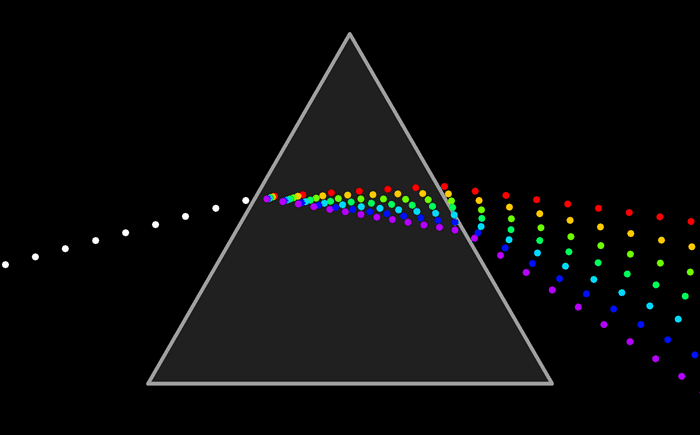
Here is a diagram of how light refracts through a prism. Each wavelength of light refracts at a different angle. White light is a mixture of all the colors in the rainbow. When it passes through a prism, each of these wavelengths is separated.
This is how refraction is calculated:

When the angle of refraction is greater than or equal to 90 degrees, the ray is completely reflected. This is called total internal reflection.
Mirrors and Lenses
Flat mirrors:
Angle of Incidence = Angle of Reflection always

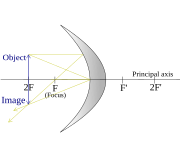
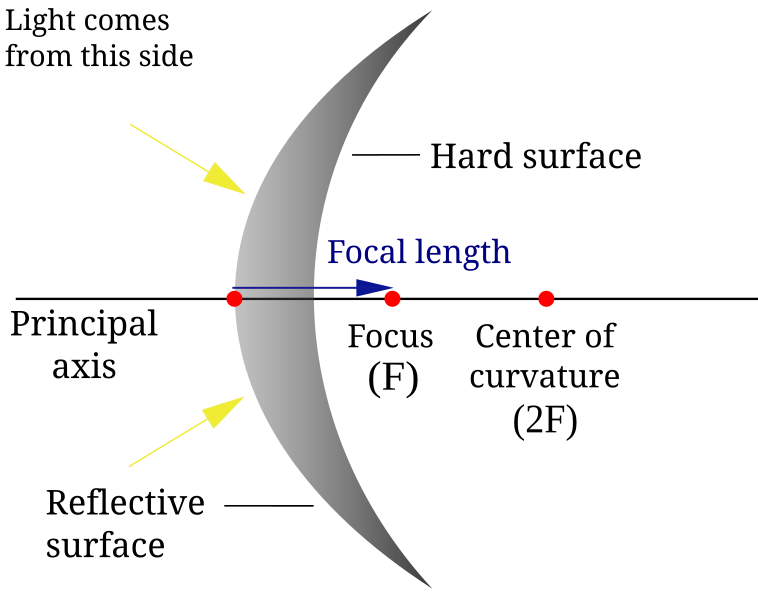
Concave mirrors:
Here is a diagram of a concave mirror:

Here are some diagrams about how images are formed (click to enlarge):
Please note that 2F=C


- When S < F, the image is:
- Virtual
- Upright
- Magnified (larger)
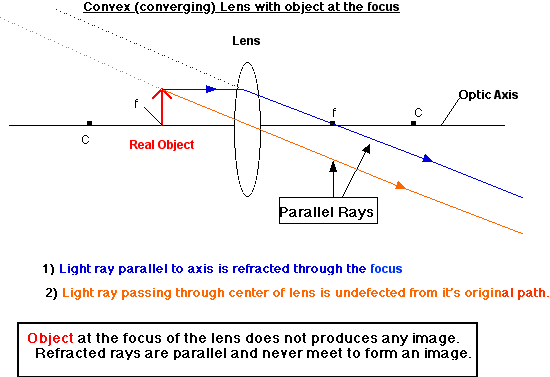
- When S = F, the image is formed at infinity.
- Note that the reflected light rays are parallel and do not meet the others. In this way, no image is formed or more properly the image is formed at infinity.
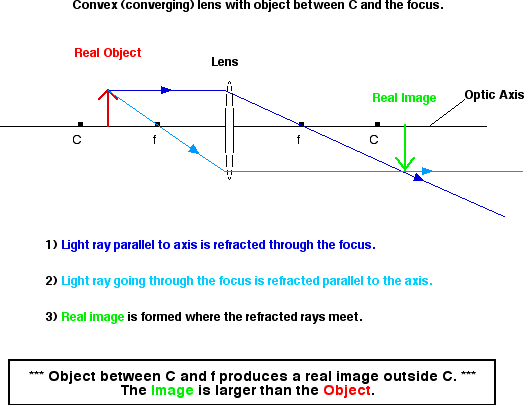
- When F < S < 2F, the image is:
- Real
- Inverted (vertically)
- Magnified (larger)
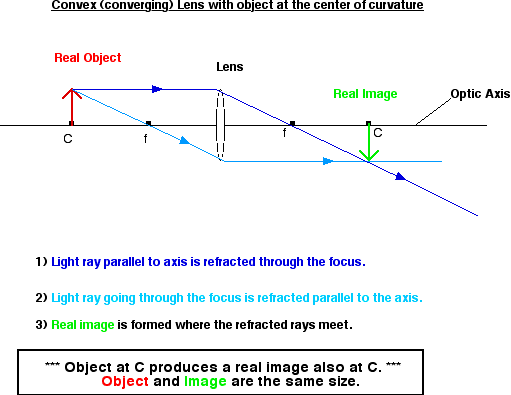
- When S = 2F, the image is:
- Real
- Inverted (vertically)
- Same size
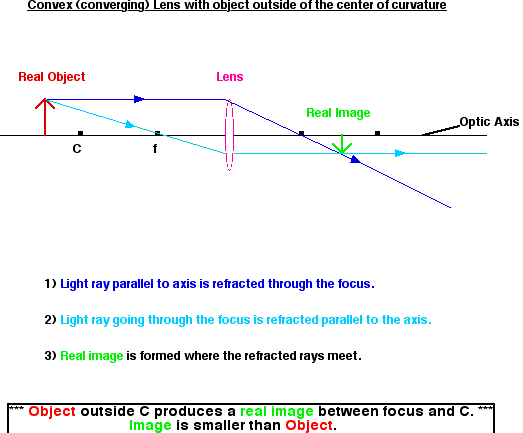
- When S > 2F, the image is:
- Real
- Inverted (vertically)
- Diminished (smaller)
The mirror equation relates the object distance (do) and image distances (di) to the focal length (f):
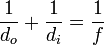 .
.
The magnification of a mirror is defined as the height of the image divided by the height of the object:
 .
.
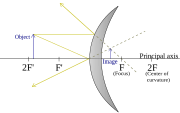
Convex mirrors:
Here is a diagram of a convex mirror:
Here are some diagrams about how images are formed:
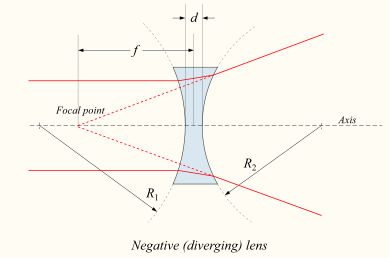
Diverging Concave Lens:
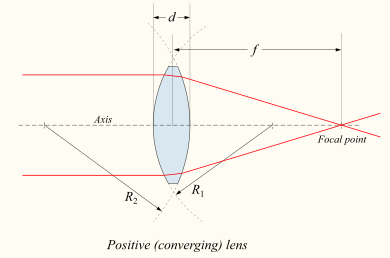
Lenses act in much the same way mirrors do, except the images are formed on the other side. The equations are the same as well.
The lens equation (which is the same as the mirror equation) relates the object distance (do) and image distances (di) to the focal length (f):
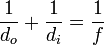 .
.
The magnification of a lens (or mirror) is defined as the height of the image divided by the height of the object:
 .
.
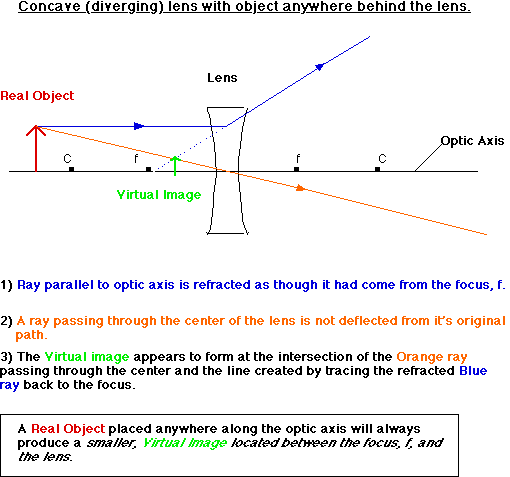
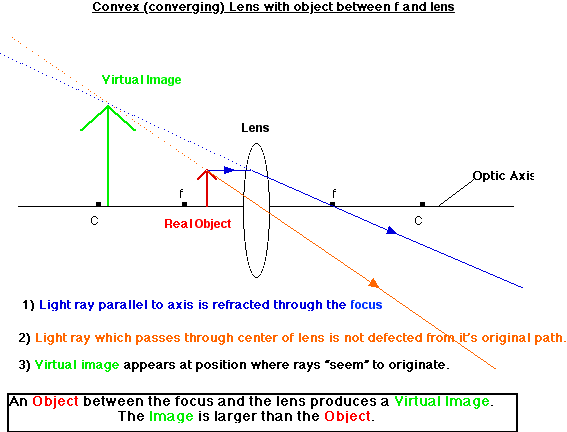
Converging Convex Lens:
2.)
3.)
4.)
5.)
Diffraction
Diffraction is the property of waves and light in which they bend around corners and obstacles. This can be observed using one of the simulators above. With the second wave simulator look at the "double slit" setup.
For more information, here is a great resource.